Browser History Examiner v1.5 is now available to download. Details of new features can be found below:
Extracting Email AddressesIt can prove vital to an investigation to quickly establish what email addresses have been used within a web browser. For example, the email addresses that have been used to log into various online services such as webmail and social media. Email addresses can be found in many different areas within the browser history. BHE now automatically extracts email addresses from a variety of sources including Saved Logins, Form History, Website Visits, Session Data, Cache Records and Favicons.
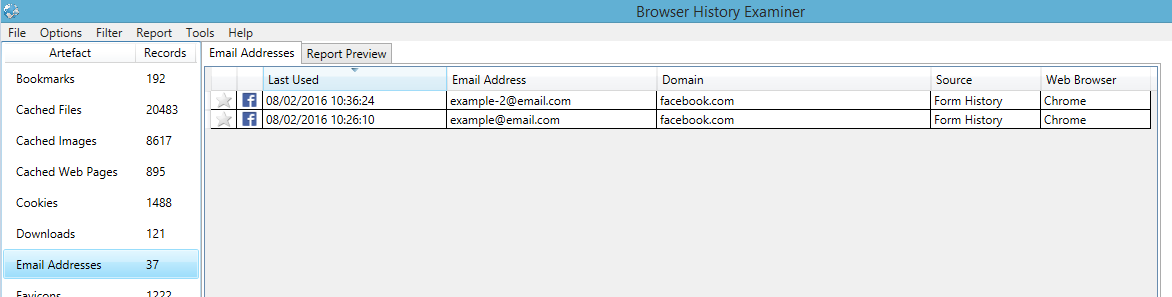 Linking Form History to Web Page URLs
Linking Form History to Web Page URLsBoth Chrome and Firefox store values entered into HTML forms in order to provide an autocomplete option the next time the web page is visited. This data can be very useful for an investigator as it may help establish usernames and email addresses used to log into various online services, even if the user has chosen not to save the associated password. However, neither Chrome or Firefox store the associated URL as part of a form entry record. BHE now automatically tries to determine the web site domain that is associated with form entry records. More details on this can be found in our blog post, "
Uncovering Web Browser User Input - Linking Form History to Web Page URLs".
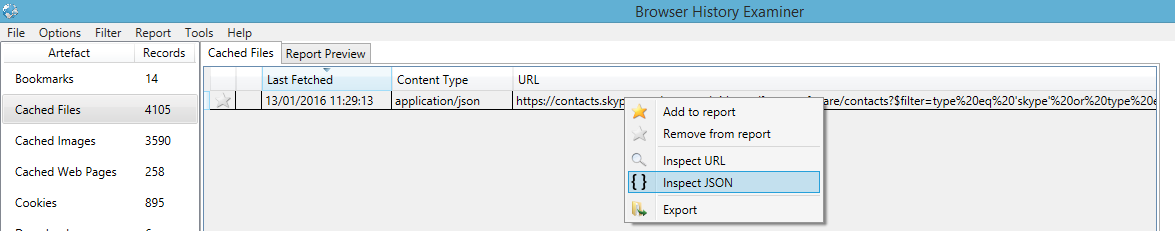
 Searching Cached JSON Content
Searching Cached JSON ContentIn a previous blog post titled "
Analysing Skype contacts in the browser cache" we discussed how useful browser artefacts are still being cached to disk. As promised in this blog post we have now extended the searching capabilities of BHE to allow keyword searches to be performed across all cached JSON content. This functionality can help uncover further hidden artefacts within the browser cache.